2025 pushed DeFi further along its maturity curve, with discernible credit cycles, growing institutional inflows, and increasingly robust trading venues. Onchain credit expansion resumed in H2 as risk appetite returned, while the ascent of RWA tokenization showed that institutions now view blockchain infrastructure as a viable distribution channel.
Trading dynamics also shifted. Perp DEXs posted ATH volumes, while spot DEX activity remained muted and largely driven by chain rotation rather than net growth. Prediction markets stayed active post-election and drew major investment.
Taken together, 2025 showed DeFi progressing toward a more durable equilibrium, with maturing primitives and expanding institutional alignment laying the groundwork for broader growth ahead.
Onchain Credit Expansion Continues
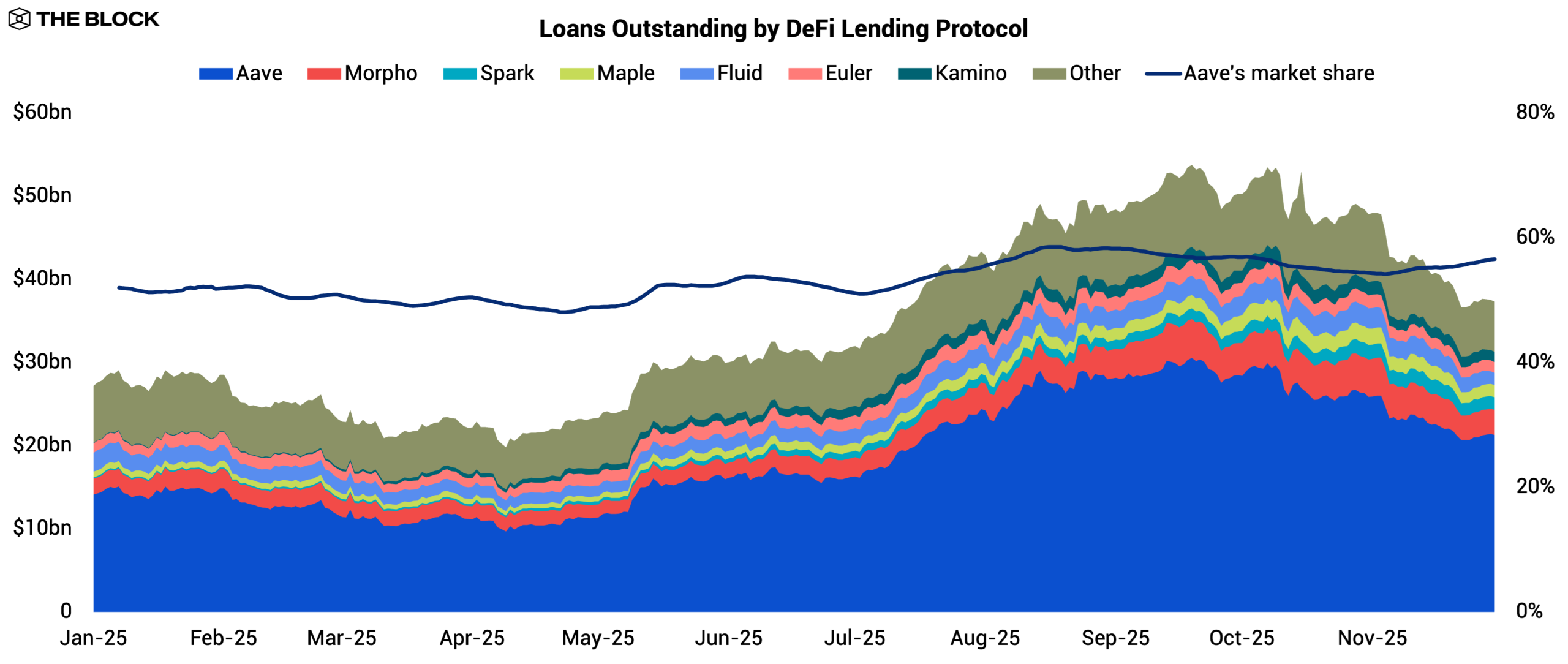
DeFi’s credit engine continued to expand in 2025, though the trajectory was uneven. Total outstanding loans across major lending protocols rose 37.2% YTD, trailing the stablecoin market cap growth of 48.1%.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama, CoinGecko
Credit contracted in H1 as borrowers remained cautious, but the trend reversed in H2 when borrowing accelerated and credit growth caught up with liquidity inflows. The full-year profile reflects a market shifting from risk aversion to reëngagement, with leverage rebuilding alongside rising digital asset valuations, followed by noticeable deleveraging in Q4 as valuations softened.
Aave strengthened its position as the dominant lending venue, with its share of total debt rising from 52.0% to 56.5%. This trend reflects Aave’s ability to retain and attract borrowing activity as liquidity returned to the system. Its core strength on Ethereum remains anchored by deep liquidity, while its multichain strategy continued to deliver. Integrations with Plasma and Linea in Q3 generated meaningful activity, resulting in $1.8 billion and $190 million in borrowed liquidity, respectively.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama, CoinGecko
Aave is also widening its distribution on multiple fronts. Horizon, its RWA-focused money market, surpassed $176 million in loans outstanding and marked a credible entry into tokenized private credit. Meanwhile, an upcoming retail-focused mobile app signaled an effort to consolidate retail demand.
At the same time, challengers gained ground. Morpho overtook Spark and grew its loans outstanding from $1.9 billion to $3.0 billion, establishing itself as the second-largest lender. Its strategy was to expand into markets that Aave was slower to serve. Morpho now supports 29 chains versus Aave’s 19. On Base, it became the largest lending market with $1.0 billion borrowed, ahead of Aave’s $539 million.
A major catalyst was Coinbase’s integration of Morpho as the infrastructure for its crypto-backed loan products. This distribution channel materially accelerated Morpho’s growth. Morpho V2 then expanded into fixed-rate lending with defined maturities, giving the protocol a differentiated product line rather than relying solely on breadth.
Maple was the black horse of the year. Its outstanding loans grew from $181 million to $1.5 billion, an eightfold increase. Maple leaned into private credit provisioning and saw strong demand for its syrupUSD pools, where users deposit stablecoins permissionlessly and receive yield-bearing tokens backed by a portfolio of short-duration, overcollateralized loans to real businesses and lenders.
syrupUSD integrated with major DeFi protocols throughout 2025, including Spark, Morpho, Fluid, and Pendle. Spark also allocated $610 million to the syrupUSD pools, which was a primary driver of its expansion. By packaging institutional private credit into accessible, liquid tokens, Maple expanded the TAM of onchain credit and captured a segment that no other major lending protocol served effectively.
Across the sector, entrenched lenders consolidated their footing while newer competitors captured new ground. Aave expanded on multiple fronts, Morpho secured a powerful distribution channel, and Maple brought private credit onchain with improved accessibility.
The outcome is a lending landscape that is both more competitive and diverse. Looking ahead, sustained growth will require access to new borrower segments and stronger distribution channels, but ultimately still depends on rising digital asset valuations to provide the collateral base for further credit expansion.
Public-Market RWAs Cross the Adoption Threshold
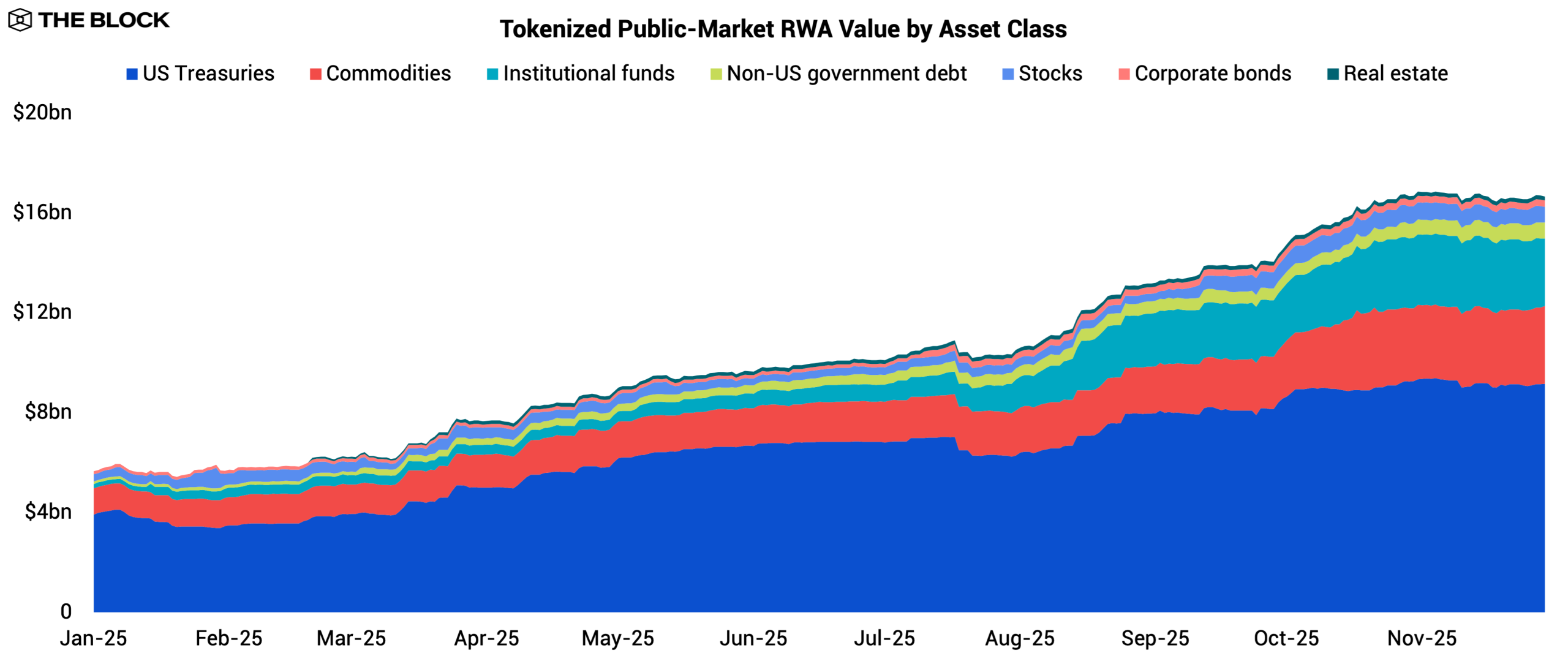
2025 was the breakout year for RWA tokenization. After stalling in the post-2022 liquidity crunch, the RWA market regained momentum. Tokenized public-market RWA value grew from $5.6 billion to $16.7 billion YTD, marking the strongest expansion the sector has seen since inception. Growth was not confined to a single asset class, as US Treasuries, commodities, and institutional funds all saw meaningful inflows driven by distinct demand catalysts.
Source: The Block, RWA.xyz
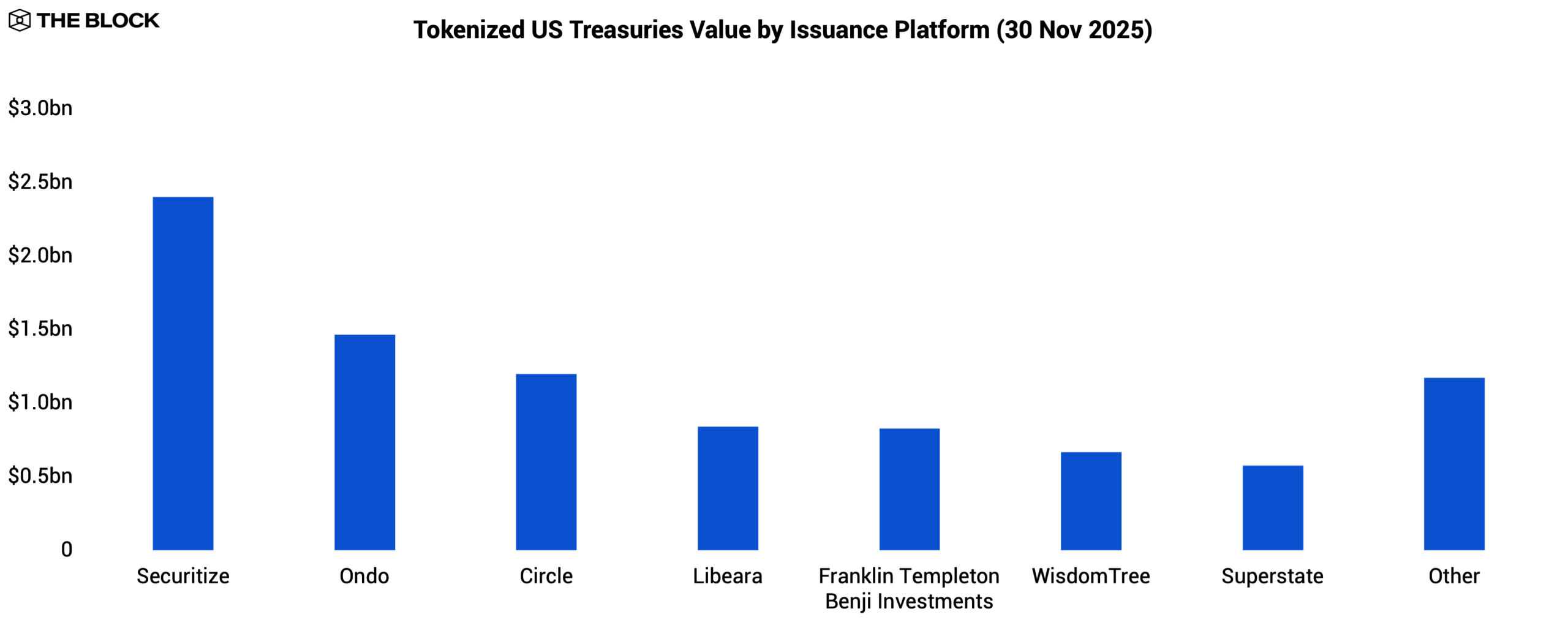
Tokenized US Treasuries remained the largest RWA category, with tokenized value rising from $3.9 billion to $9.2 billion YTD. The standout instrument was BlackRock’s BUIDL, issued via Securitize, which reached $2.3 billion in AUM. BlackRock’s presence served as a credibility anchor for institutions previously hesitant to adopt tokenized fixed-income products.
Source: The Block, RWA.xyz
A growing set of onchain products now builds directly on top of BUIDL. Ethena’s USDtb and Ondo’s OUSG both leverage BUIDL as a core reserve asset, effectively making it the backbone collateral layer for an expanding class of tokenized cash and Treasury products.
Tokenized commodities remained the second-largest category, with tokenized value rising from $1.1 billion to $3.1 billion YTD, nearly a threefold increase. This expansion was overwhelmingly driven by tokenized gold products such as Tether’s XAUT and Paxos’ PAXG. XAU’s +60.7% YTD performance and its move to new ATHs drew retail inflows from speculators seeking alternative exposure without leaving the DeFi ecosystem amid changing macro conditions.
Tokenized institutional funds were the clear rising star this year. Its tokenized value surged from $170 million to $2.7 billion YTD as crypto-native investors diversified beyond digital assets. Anemoy’s JAAA led the segment with $1.0 billion in AUM, seeded by Grove, an institutional-grade credit infrastructure protocol within the Sky ecosystem. JAAA provides onchain exposure to AAA-rated CLO tranches aimed at capital preservation and steady income.
Other notable tokenized funds included the Superstate’s USCC, which provides access to a crypto carry trade strategy and accumulated $440 million in AUM. Meanwhile, Blockchain Capital’s digital venture fund, BCAP, reached $359 million in AUM. These products demonstrate that RWA tokenization can support discretionary and actively managed strategies, not just passive fixed-income exposures.
Several smaller categories also gained traction but remained niche, including non-US sovereign debt, public equities, corporate bonds, and real estate. Limited liquidity and operational constraints likely kept these segments small, though early experimentation suggests that issuers are testing broader asset classes as infrastructure matures.
The defining theme of 2025 was that tokenization finally became a distribution technology that institutions were willing to use at scale. Public blockchains proved to be increasingly efficient venues for issuance, settlement, and investor access, while interoperability with major DeFi protocols improved the utility of tokenized RWAs beyond simple buy-and-hold use cases.
Looking ahead, continued institutional participation is likely to deepen as the product spectrum widens. Further integration with lending markets and onchain treasury systems will increase both the usefulness and appeal of RWAs, positioning tokenization as a central pillar of digital capital markets.
Perp DEXs Break Records Amid New Entrant Push
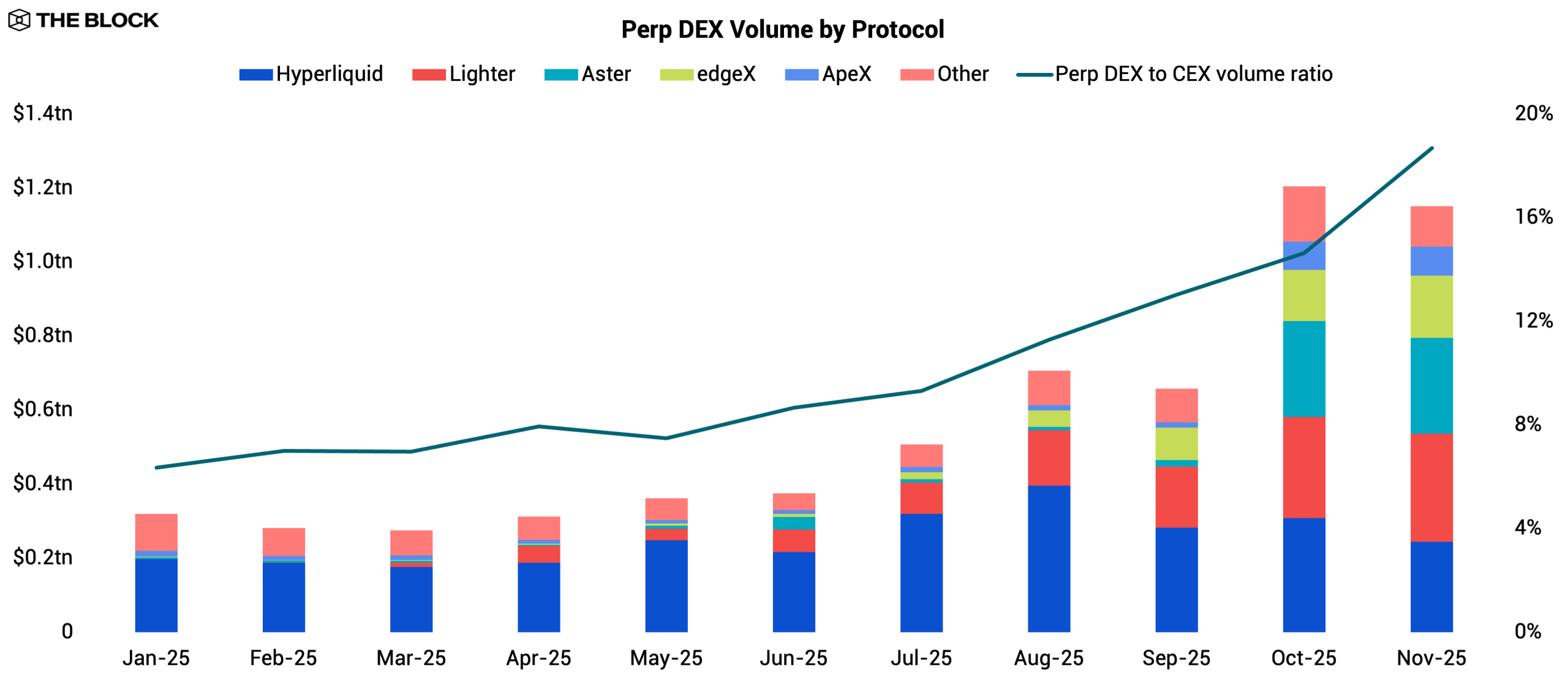
2025 was a defining year for onchain derivatives. The DEX-to-CEX perpetual futures volume ratio tripled from 6.3% to 18.7%, marking a significant shift in a market long dominated by centralized venues. This trend reflects a narrowing efficiency gap as execution speed, liquidity depth, and overall user experience on perp DEXs improved enough to accommodate more sophisticated traders. October recorded the highest onchain derivatives volume to date, propelled by the sharp market drawdown on October 10.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama
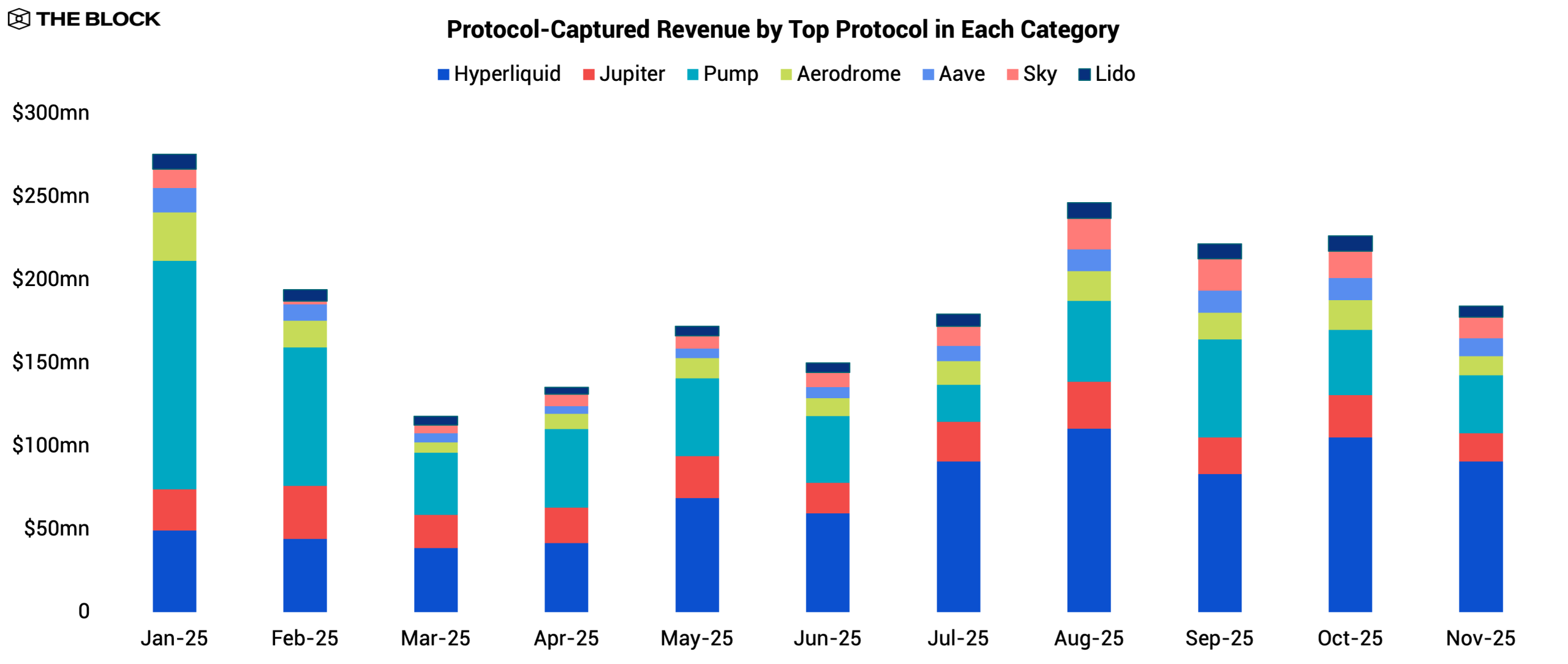
Hyperliquid entered the year as the undisputed leader among perp DEXs. Its annualized volume rose from $564.7 billion in 2024 to $3.0 trillion in 2025, and it consistently remained one of the most profitable protocols in DeFi when measured by protocol-captured revenue, excluding supply-side revenue paid to liquidity providers. Its moat was built on speed, deep organic liquidity, and a sticky user base. But by mid-year, Hyperliquid’s dominance began to face real pressure from a new wave of well-funded challengers.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama
Lighter emerged in H2 as the most aggressive new entrant. Its zero-fee model attracted crypto-native traders, while its multistage points system fed directly into future airdrop eligibility and pulled in incentive farmers. Lighter capped off its breakout year by closing a funding round in Q4 that included a rare strategic participation from Robinhood, signaling potential future integration or alignment between centralized trading apps and onchain derivatives infrastructure.
Aster also gained relevance in Q4, driven largely by its affiliation with Binance. Backed by YZi Labs (formerly Binance Labs) and closely aligned with the BNB Chain ecosystem, Aster benefited from distribution channels few protocols can access. It also undercut Hyperliquid’s trading fees by a narrow margin, positioning itself as a lower-cost alternative. Its multistage points system mirrored Lighter’s approach and helped accelerate user acquisition. This combination of distribution, cost advantages, and incentives made Aster one of the protocols capable of contending with Hyperliquid’s lead.
Across the segment, the competitive landscape is intensifying. Hyperliquid remains the incumbent, but the influx of capital and incentives suggests its lead is not guaranteed. The dynamic resembles prior cycles, most notably the rise and fall of dYdX, where early dominance did not translate into permanent market share.
Looking ahead, the arms race is likely to continue. Well-funded challengers will keep leveraging low-fee structures, points systems, and strategic partnerships to chip away at Hyperliquid’s position. But this competition elevates the overall user experience and continues to close the gap with centralized counterparts.
Prediction Markets Stay Relevant Post-Election
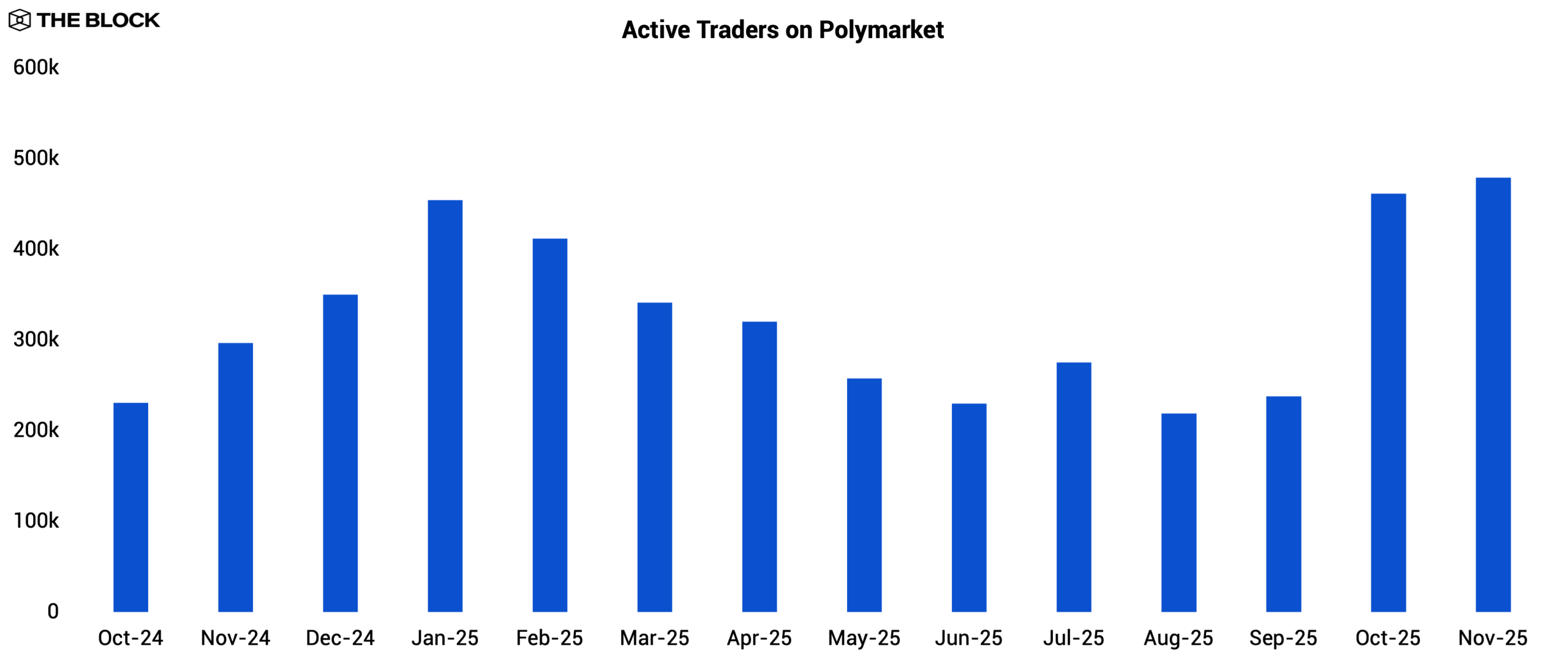
Prediction markets experienced a slowdown after the US presidential election in November 2024, with volume falling off in the months that followed. Even so, the election cycle demonstrated the potential of prediction markets to a broader audience, and monthly active traders on Polymarket rose post-election as users stayed for newly listed event markets despite lower overall trading volume.
Source: The Block
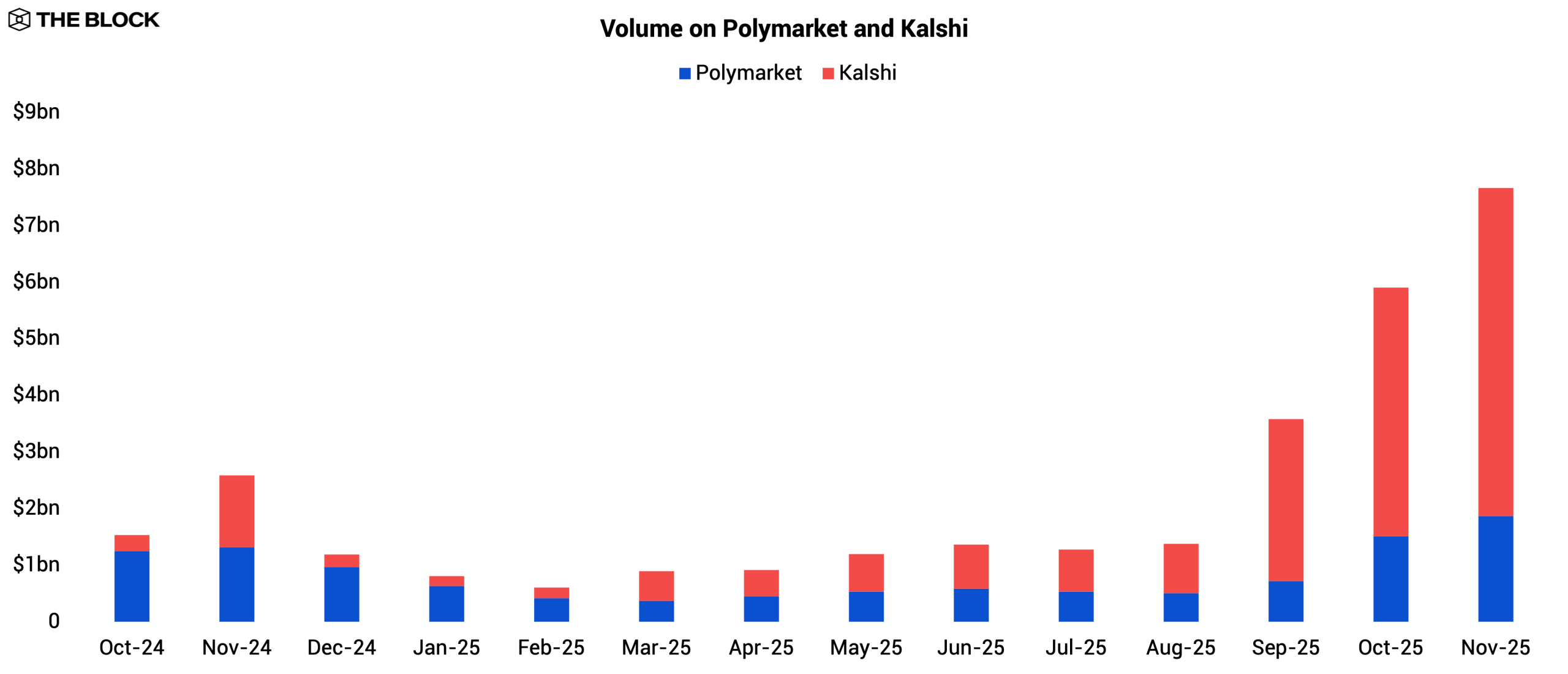
Trading activity rebounded heading into September 2025 as new catalysts emerged. This shift was driven by Kalshi’s partnership with Robinhood, which opened a substantial retail distribution channel, and by the commencement of major sports seasons, which funneled traffic toward Kalshi’s sports-event markets.
Source: The Block, Kalshi
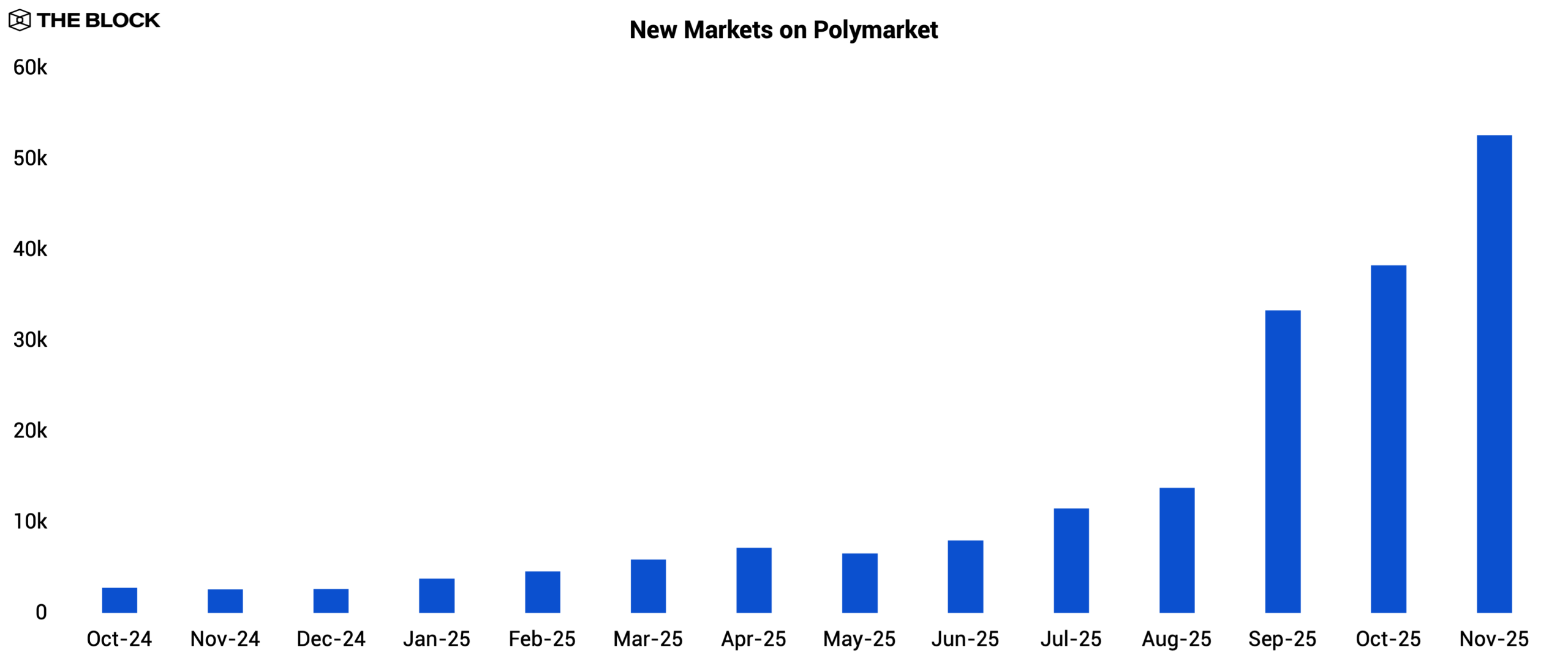
This competitive pressure appears to have prompted Polymarket to accelerate the pace of new market creation beginning in September to retain user engagement. Both platforms then posted record volumes in November: Kalshi processed $5.8 billion, while Polymarket reached $1.9 billion.
Source: The Block
Kalshi operates as a CFTC-regulated centralized platform, whereas Polymarket is fully onchain. In 2025, Polymarket acquired a CFTC-licensed derivatives exchange and clearinghouse for $112 million, enabling it to reënter the US market after receiving CFTC approval in November.
Both platforms secured major investment rounds in 2025, underscoring growing institutional conviction in event contracts as an emerging derivatives category. Polymarket raised $2 billion in October from Intercontinental Exchange, the parent company of the NYSE, at a $9 billion valuation. Meanwhile, Kalshi raised over $1 billion across multiple rounds during the year, putting its latest valuation at $11 billion. The size and pedigree of these investors mark a turning point in the sector’s legitimacy.
Looking ahead, both well-funded giants are now positioned to go head-to-head into the 2026 US midterm cycle, a period associated with elevated volume. With strengthened balance sheets, resolved regulatory hurdles, broader distribution, and expanding product breadth, the upcoming election cycle is likely to generate the largest prediction market activity to date.
Spot Trading Activity Shifts as Launchpad Hype Fades
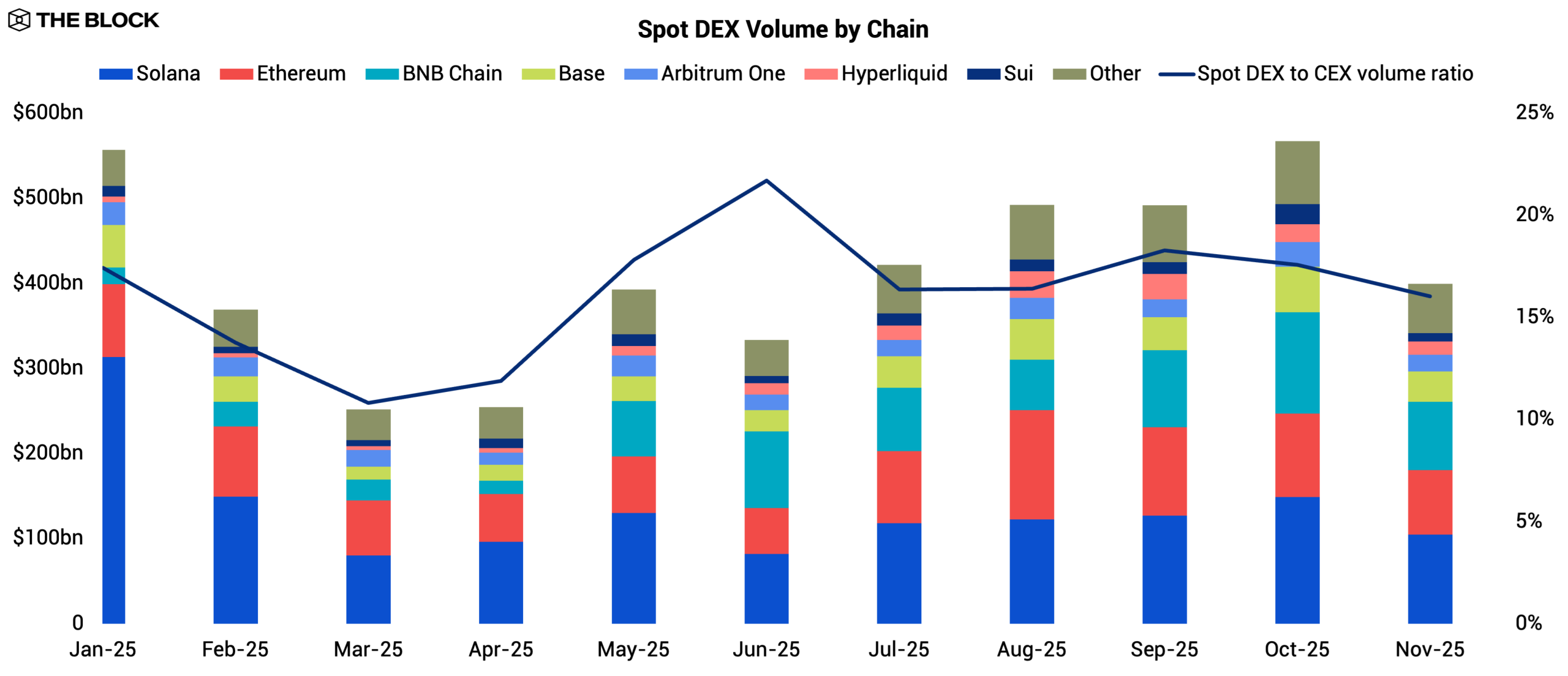
Spot DEX activity in 2025 lacked a clear upward trajectory. Volumes fluctuated throughout the year but ultimately failed to meaningfully outpace broader market growth. The most striking shift came from chain-level rotation: Solana’s monthly spot trading volume, which began the year at $313 billion in January, fell to $104 billion by November, a 66.7% decline that marked the unwinding of last year’s retail-driven memecoin mania.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama
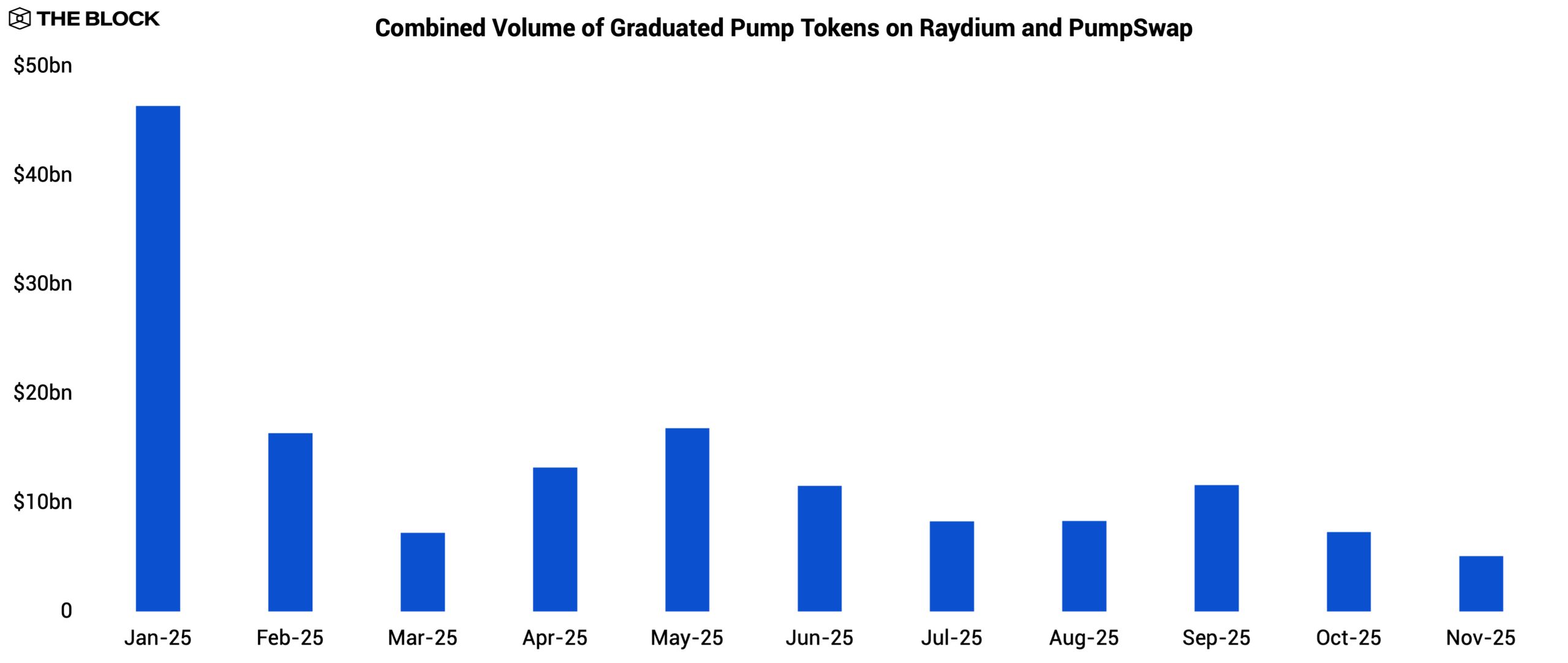
Pump, the dominant Solana launchpad of 2024, saw its graduated token trading volume on Raydium and PumpSwap crater from $46.4 billion in January to $5.1 billion in November, a 89.0% drawdown. Retail enthusiasm for launchpad-incubated tokens collapsed, and the churn-and-flip cycle that had propelled Solana’s spot DEX activity in 2024 did not reappear at the same scale in 2025.
Source: The Block, DeFiLlama
Meanwhile, BNB Chain moved in the opposite direction, with its monthly spot trading volume more than quadrupling from $19.3 billion in January to $80.3 billion in November. As Solana’s retail liquidity evaporated, speculative flows did not disappear but migrated to BNB Chain. BNB Chain absorbed a sizable portion of retail speculation, with a long-standing microcap trading culture that proved resilient as interest in Solana memecoins cooled.
Across the ecosystem, the DEX-to-CEX spot volume ratio hovered below 20% throughout the year, underscoring that the structural efficiency gap in spot trading remains largely unchanged, a sign that spot DEXs have reached maturity on the infrastructure side. The general appetite for onchain spot trading did not vanish in 2025 but simply reshuffled. Unless a new catalyst emerges to drive sustained token turnover, the trajectory of spot DEX activity will hinge on shifts in retail sentiment shaped by broader macro conditions.
Composability Amplifies Systemic Risks
Composability has long been one of DeFi’s defining strengths. Protocols can integrate with each other permissionlessly, assets can be rehypothecated across venues, and new financial primitives can be built by stacking existing ones like modular components. It improves capital efficiency, enables rapid innovation, and creates powerful network effects.
But it also creates tight coupling between systems. When assets or assumptions break within a single protocol, their effects can propagate across the ecosystem. The Stream Finance incident in November 2025 became the clearest example of how this same strength can evolve into a vector for systemic risk.
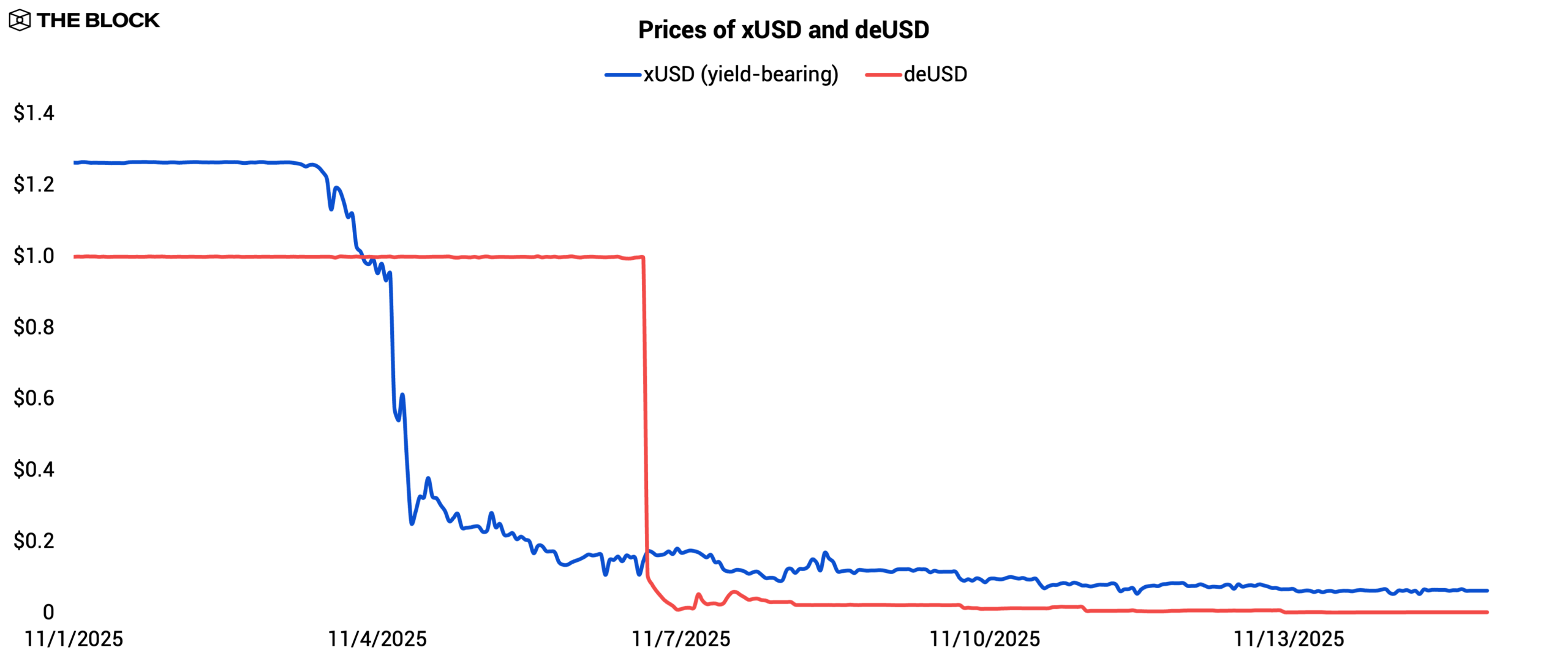
Stream allowed users to deposit assets in exchange for xUSD, a yield-bearing stablecoin marketed as being backed by market-neutral strategies run by external fund managers. That assumption collapsed when one of the appointed fund managers disclosed a $93 million loss in executing strategies with allegedly minimal directional exposure, leaving xUSD materially undercollateralized. Stream immediately halted deposits and redemptions, and xUSD began to depeg as confidence evaporated and liquidity fled secondary markets.
The depeg quickly exposed the fragility of composability. Elixir’s stablecoin, deUSD, was partially backed by xUSD-denominated exposure, while xUSD itself held deUSD in its collateral mix, creating a circular collateralization loop that became untenable once xUSD breached parity.
Source: The Block, CoinGecko
Shortly after xUSD lost its peg, Elixir froze deUSD minting and redemptions, and deUSD depegged as markets repriced the interconnected exposure. What began as an isolated failure of an external fund manager cascaded into a multi-protocol unwind solely because the two stablecoins were tightly interlinked through composable collateral frameworks.
The contagion also spread to lending protocols. Several money markets on Morpho and Euler had hardcoded a $1 collateral value for xUSD. This design was intended to prevent accidental liquidations during temporary market volatility, but it backfired once the depeg became persistent. Borrowers were able to take out loans against xUSD at full face value even as the token traded well below par, creating pockets of bad debt that the protocols were forced to absorb.
Composability is not inherently problematic, but it requires risk controls that assume any one component might fail at any moment. Looking ahead, DeFi protocols must account for cross-protocol exposures and design frameworks that can respond to black swan events. Composability remains one of DeFi’s greatest advantages, but without stronger guardrails, it will continue to magnify systemic risks just as efficiently as it accelerates innovation.
Outlook
The progress made in 2025 positions DeFi for a steady expansion phase. Institutional investment across RWAs, derivatives, and prediction markets reflects rising confidence in onchain infrastructure. These systems are approaching parity with their centralized counterparts in execution and reliability, shifting competition toward distribution and regulatory positioning rather than technology alone.
Even so, macro conditions remain the primary driver of scale. Credit creation, market depth, and retail participation will hinge on broader liquidity conditions. If global liquidity turns supportive, DeFi’s mature infrastructure could translate into more durable growth. Still, sustained expansion will require stronger risk management to mitigate systemic vulnerabilities inherent to a composable ecosystem.
Disclaimer: The Block is an independent media outlet that delivers news, research, and data. As of November 2023, Foresight Ventures is a majority investor of The Block. Foresight Ventures invests in other companies in the crypto space. Crypto exchange Bitget is an anchor LP for Foresight Ventures. The Block continues to operate independently to deliver objective, impactful, and timely information about the crypto industry. Here are our current financial disclosures.
© 2025 The Block. All Rights Reserved. This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.